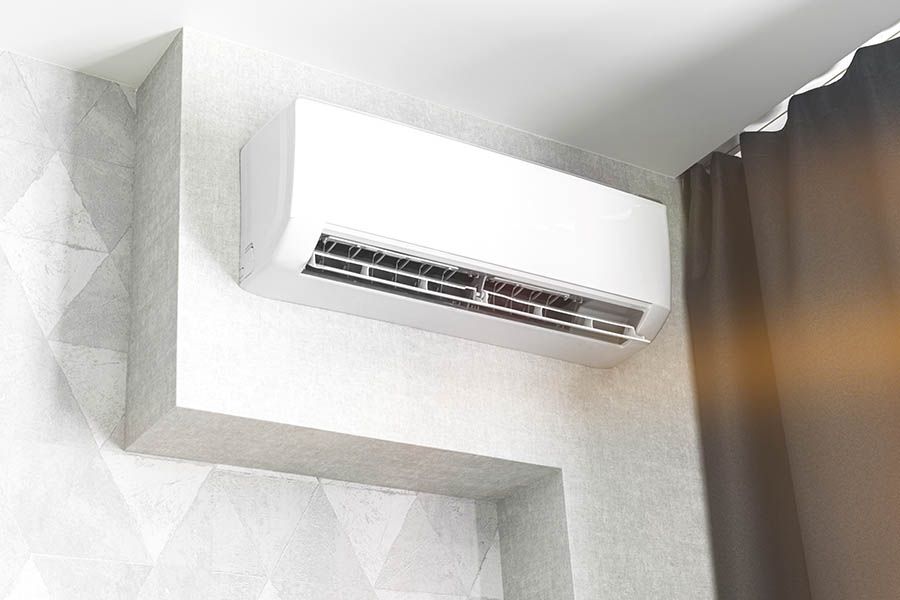
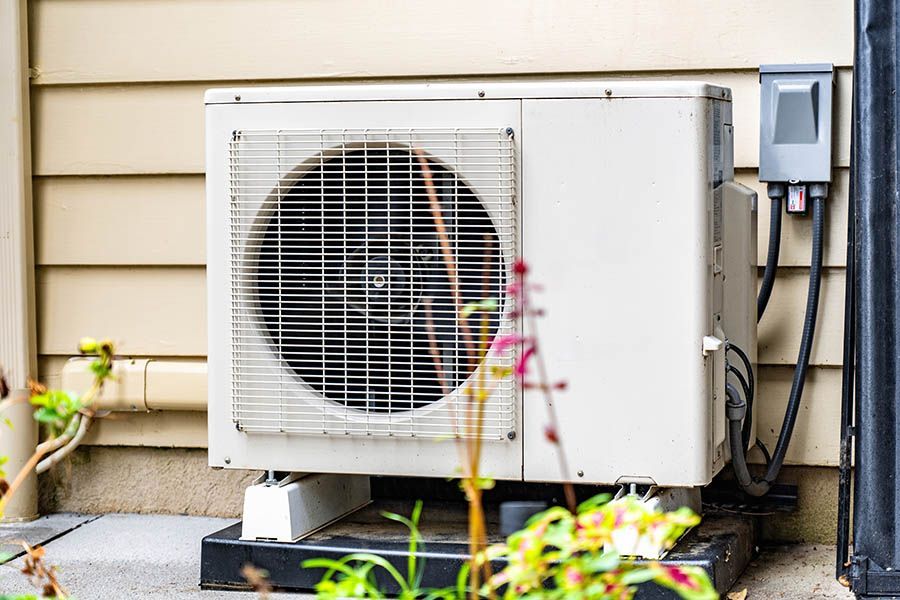
A heat pump is able to transfer thermal energy from inside to outside and also from outside to inside. A heat pump works as an air conditioner by transferring heat from inside to outside. Heat pumps can also be used for heating. When heat pumps are used to heat a building the energy or heat is transferred from outside to inside. Mini Splits are commonly ductless and for this and other various reasons they are highly efficient and rely on electricity to provide heating and cooling thereby reducing the demand on fossil fuels. Typically it has been measured that 1kWh of electricity can transfer 3-6 kWh of thermal energy into a building, this is amazing and highly efficient as opposed to an oil boiler or a window AC unit both of which minisplits are 3-4 times more efficient over.
Heat pumps are filled with refrigerant, this gas/liquid is highly controlled by the EPA and you must be licensed by the EPA to purchase and handle the current models on the market. Most of todays heat pumps are currently working with 410-a refrigerant. The heat pumps produce heat by taking the liquid outside and compressing it, making it hot. This hot liquid is transferred inside through a series of copper tubing that must connect the indoor and outdoor units. This hot liquid passes though a coil and is blown with or without ductwork. To cool your home, the heat pump works in the opposite, by compressing the indoor hot liquid and sending it outside to be cooled by the large coil and fan at the outdoor compressor.
It is possible that heat pumps could be used in the future to replace most oil and gas fired heating equipment to create a lower carbon footprint. Air sourced heat pump minisplits are relatively inexpensive to install and historically have been the most widely used type of heat pump, modern heat pumps with a low temperature designation are able to provide heat inside your home even when the outdoor temperatures reach down to -15 degrees.
In traditional air sourced heat pump systems, the system has a vapor compression device, a compressor and the system includes a reversing valve so that the direction of thermal energy, heat, or cooling, can be reversed. The energy efficiency of a heat pump is measured in SEER – Seasonal Energy Efficiency Rating a heat pump must meet a SEER rating of 14.5 to qualify for an Energy Star rating.